Sales funnels
Sales Funnel: What It Is, How It Works & Stages (2026 Mega Guide)
19 January 2026
Anna P

The concept of the sales funnel is not new. The original model was developed in 1898 by E. St. Elmo Lewis. But let’s be honest: if you try to apply a 19th-century sales funnel model to a 2026 digital economy, you are going to be outdated, and you are going to lose money.
Lewis’s model assumes a captive audience moving sequentially down a gravity-fed chute — Attention, Interest, Desire, Action (AIDA). The modern reality, however, is a non-linear neural network where the buyer's journey loops, inverts, and branches based on behavioral triggers that were inconceivable a century ago.
The days of easy sales have been replaced by privacy legislation, predictive AI algorithms, and a hyper-skeptical consumer base that validates before they commit. Today, a successful sales funnel is a sophisticated and data-driven ecosystem. It functions like a high-performance engine. Whether you are running a lean direct-to-consumer operation or managing a global enterprise sales department, you need to understand how to adapt and secure explosive business growth.
Let's dismantle the traditional sales funnel, examine why marketing funnels have evolved, and show you how to build a system that turns potential customers into high-value brand advocates using the latest tools and strategies.
Modern Funnel vs. Classic Funnel
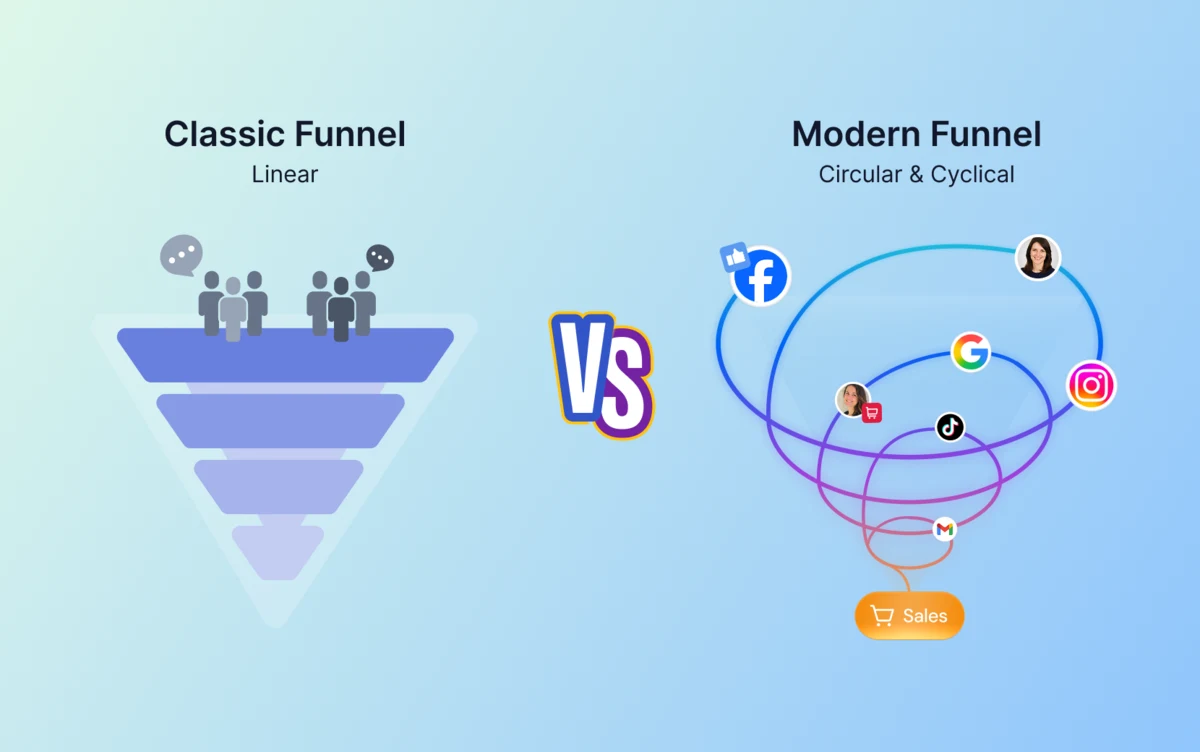
For decades, the sales funnel was depicted as an inverted pyramid. You pour a lot of prospective customers in at the top, and gravity pulls a few paying customers out at the bottom. That model assumes the customer journey is linear. It assumes a person sees an ad, clicks it, and buys immediately. It assumes humans are rational robots.
Reality of 2026
In 2026, the buying process is messy, chaotic, and heavily influenced by social proof. Consider the journey of a modern buyer — let's call her Sarah.
Awareness: Sarah sees a short-form video on TikTok about a new barista-grade coffee machine. She likes the aesthetic but keeps scrolling.
Engagement & capture: Two days later, an AI-optimized retargeting ad finds her on Instagram. She clicks through to your product page. She isn't ready to spend $600 yet, but when an exit-intent modal offers a "Barista’s Guide to Espresso & 10% Off," she enters her email address to send the code to her inbox.
Churn: Immediately after entering her email, a text message distracts her. She closes the browser tab without purchasing.
Social validation: A week later, still considering the purchase, she searches Reddit for "best home espresso machines 2026" and sees your brand validated by fans in a thread.
Conversion: The next morning, she receives an automated browse abandonment email from you reminding her of the 10% code she saved for later.
Transaction: She finally purchases via her mobile device while waiting for an Uber.
If you treat your sales efforts as a simple numbers chase where you just need more volume at the top, you will burn through your ad budget attempting to force a linear path that doesn't really exist. The way to purchase has many routes and bumps (physical distractions and informational noise), so it requires an agile sales process.
A proper sales funnel today is also circular. It focuses on user retention and customer lifetime value. It doesn't end at the sale; the sale is arguably where the real sales funnel work begins. The modern funnels are powered by sales automation, content marketing efforts, and hyper-personalized landing pages to guide the user through this web. They are digital sales teams that never sleep, ensuring that every customer interaction moves the needle toward revenue.
What is a Sales Funnel? (Definition for 2026)
A sales funnel is the visual and strategic representation of the journey a customer takes from discovering your brand to purchasing your product. It maps out the sales process step-by-step, allowing you to identify where you are losing money.
However, in the context of high-growth e-commerce and digital marketing, a sales funnel is more specific. It is a deliberate series of web pages and emails that filter traffic and maximize average order value.
Distinction: Pipeline vs. Funnel
People often confuse a sales pipeline with a sales funnel. They share the same DNA, but optimize for different outcomes.
Sales funnel is about the customer. It represents the volume of potential customers at each stage of the buying decision. It is a numbers game involving conversion rates across the aggregate audience.
Sales pipeline is about the seller (mostly in B2B). It tracks where specific deals (e.g., "Contract with Acme Corp") are in the sales cycle for sales reps to act upon.
For an e-commerce brand, your sales funnel strategies replace the manual work of sales reps. Your website, your ads, and your emails are the sales team.
Three Pillars of a Functioning Funnel
A well-defined, automated sales funnel does three jobs:
Filters: It disqualifies people who aren't a fit. You don't want to waste ad spend retargeting people who can't afford your product or don't need it.
Educates: It moves target customers from problem-aware ("I have back pain") to solution-aware ("I need an ergonomic chair") to product-aware ("I need your ergonomic chair").
Monetizes: It uses psychological pricing and packaging options, like bundles, quantity breaks, and one-click upsells, to extract maximum value from the transaction.
Why Funnels Matter More Than Storefronts
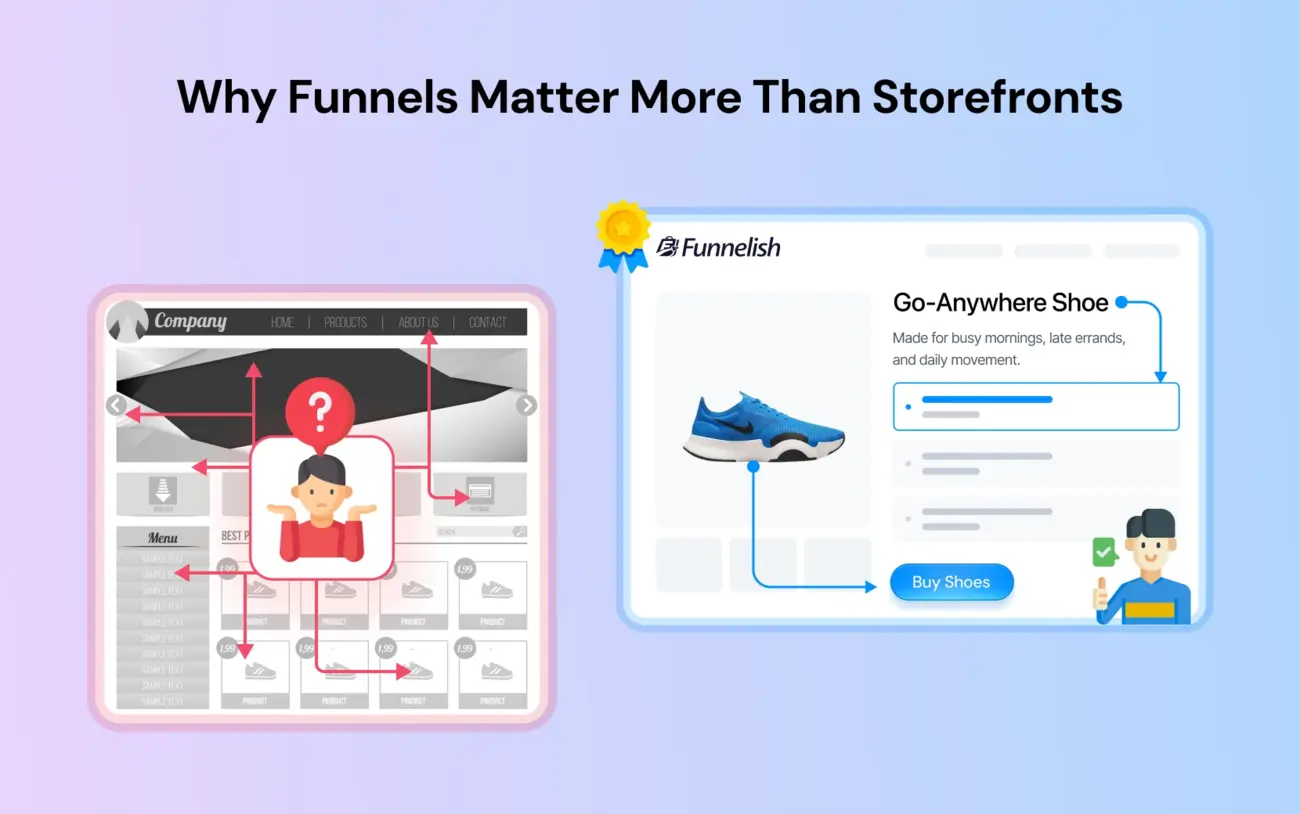
You might ask, "Why do I need a funnel if I have a really nice website?"
The answer lies in the psychology of choice. A standard website is a digital catalog. You send traffic to a homepage with a navigation bar, an About Us page, a blog, a contact form, and fifty different products. When a visitor lands there, they have to do the work. They have to search, filter, compare, and decide.
Paradox of Choice
Research by psychologist Barry Schwartz shows that when potential buyers are presented with too many options, they experience decision fatigue. Instead of feeling liberated, they feel paralyzed. They freeze. They leave.
If you send paid traffic to a homepage, you are asking the customer to navigate a maze. Most won't bother.
Funnel Advantage
A sales funnel flips this dynamic. It is a guided path, more like a concierge service than a warehouse.
Focus: It removes navigation bars, footer links, and social icons. The user has only one path forward.
Relevance: It matches the pain points mentioned in the ad to the headline on the page. If the ad talks about acne scars, the landing page headline isn't "Welcome to our Store," it is "Finally, a Solution for Acne Scars."
Speed: It directs the user to a single decision stage: buy or leave.
Getting this control is vital. You cannot optimize a chaotic homepage effectively because there are too many variables. You can, however, optimize a funnel. By controlling the path, you control the sales funnel metrics and can predict revenue with mathematical precision.
Sales Funnel Stages
While the tactics change, the psychological framework of the sales funnel stages remains rooted in human behavior. We still typically use the AIDA model in slightly different terms, and for 2026, we must add a critical fifth stage: Loyalty.
Stage 1: Awareness
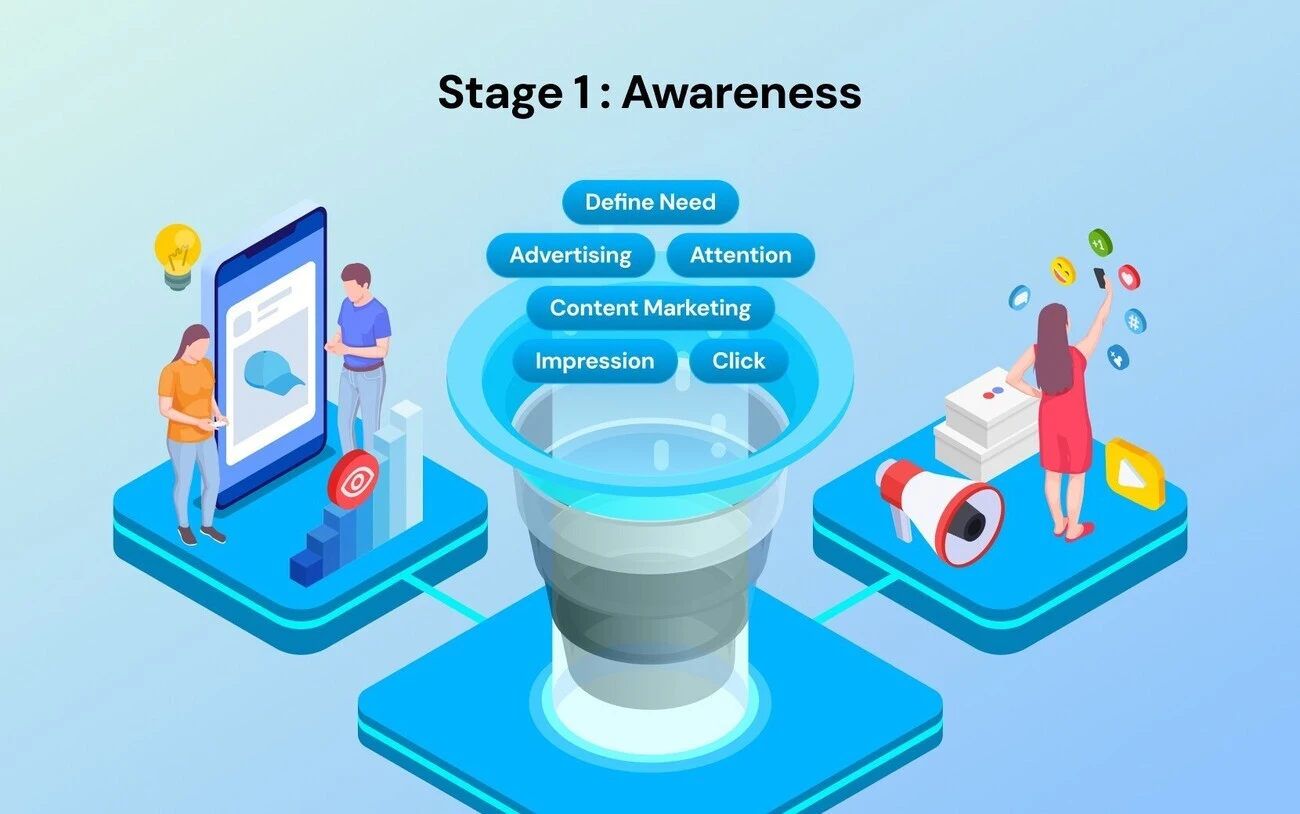
The awareness stage is the widest part of the funnel. Here, prospective customers realize they have a problem or a desire. They are not looking for your brand yet; they are looking for answers to their symptoms.
Customer's mind: "My energy levels are low in the afternoon. Why is this happening?"
Goal: Capture attention and stop the scroll.
Tactics: Social media advertising (TikTok/Reels), content marketing (SEO blogs answering questions), influencer partnerships, and viral short-form video.
Metric: Impressions and click-through rate.
Stage 2: Interest
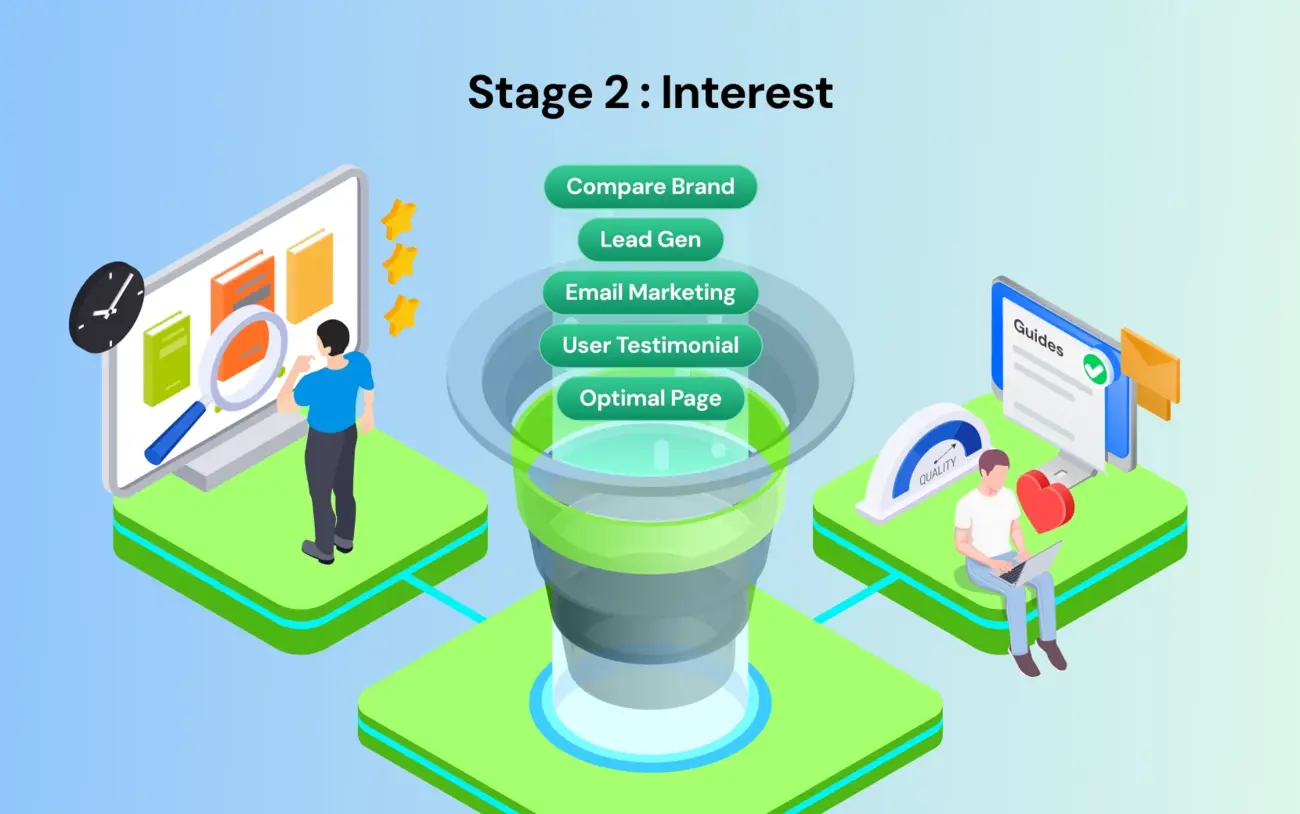
The prospect knows they have a problem and is now researching solutions. They found your brand, but they are also looking at your competitors. Here, marketing campaigns must pivot from hooking attention to providing education.
Customer's mind: "Okay, I need a green juice supplement. Should I buy Brand A or Brand B?"
Goal: Build trust and establish authority.
Tactics: Lead generation magnets (quizzes, free guides), social media retargeting with user testimonials, and educational email marketing sequences.
Metric: Opt-in rate and time on page.
You can learn more about lead generation magnets and hacks in our latest post: 10 D2C Marketing Trends in 2026 Funnel Strategies from Top Brands to Scale Profitably
Stage 3: Consideration
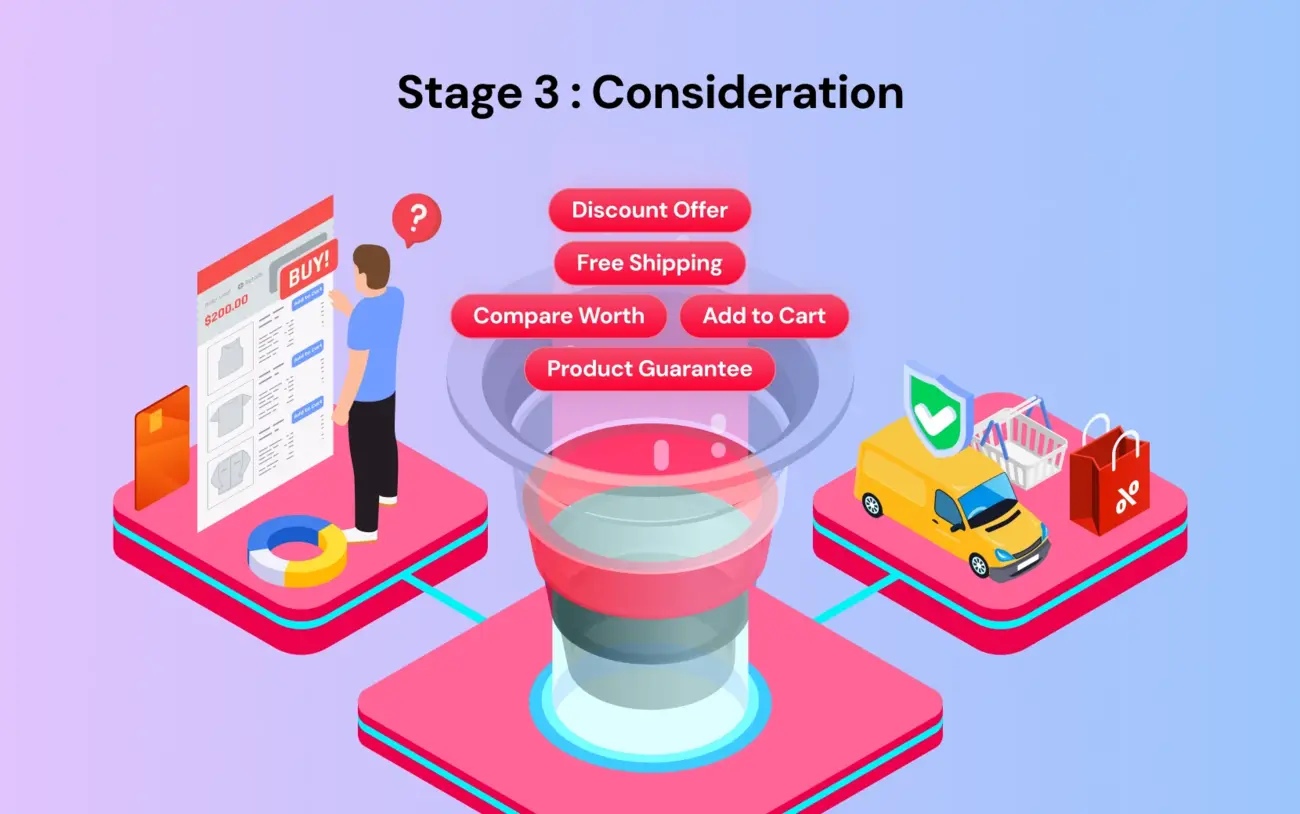
The customer is ready to buy. They are holding their credit card, but they have last-minute objections. Is the price right? Is shipping fast? What if it breaks?
Customer's mind: "I want this, but $50 feels expensive. What if I don't like the taste?"
Goal: Overcome objections and lower friction.
Tactics: Comparison charts vs. competitors, free shipping offers, limited-time discounts, and clear money-back guarantees. High-speed landing pages built on Funnelish can also help prevent bounce caused by slow loading.
Metric: Add-to-cart rate.
Stage 4: Conversion

The transaction happens. The prospect becomes a paying customer. In a basic sales funnel, this is the end. In a successful sales funnel, this is where profit happens via upsells.
Customer's mind: "I just bought the juice. I feel good about this decision."
Goal: Maximize average order value.
Tactics: One-click upsells (offering a shaker bottle), order bumps (adding rush shipping), and cross-sells.
Metric: Conversion rate and AOV.
Stage 5: Loyalty
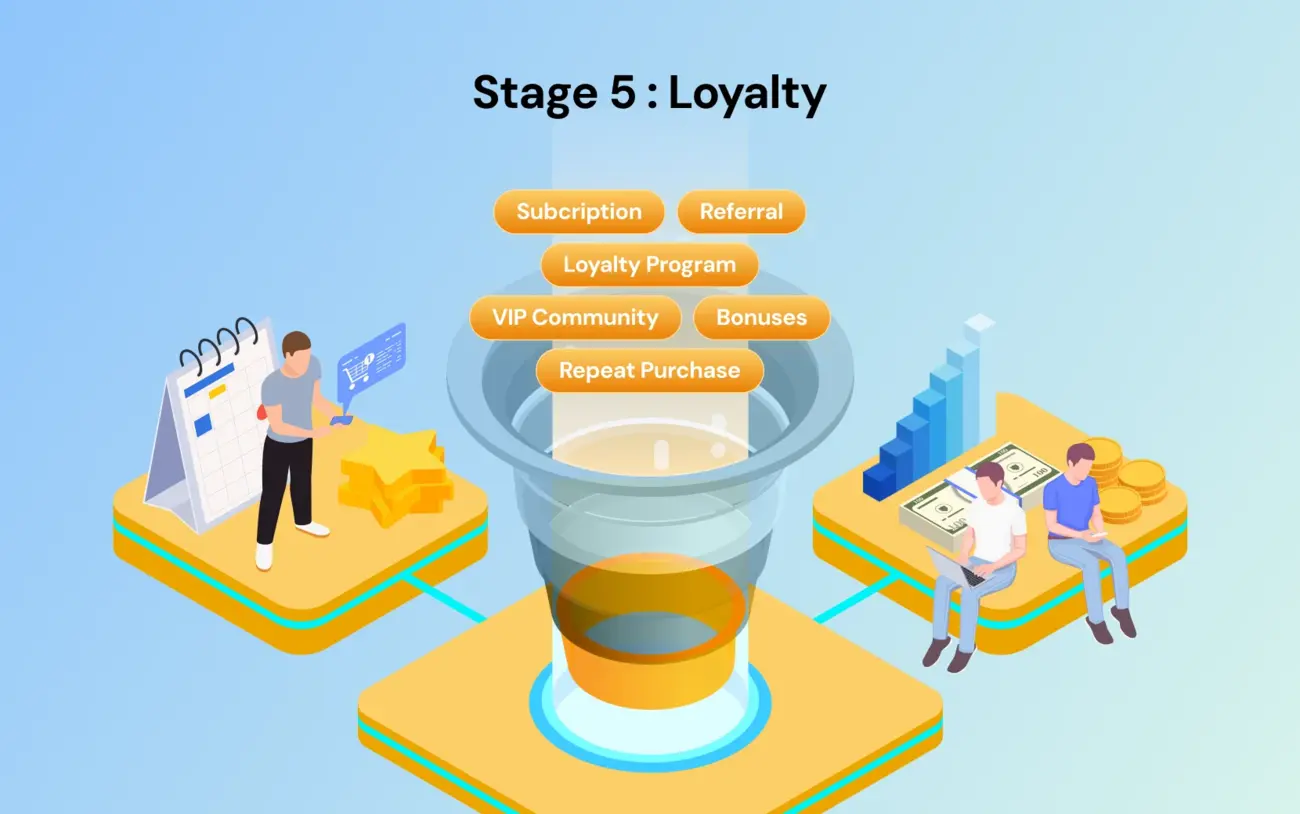
The sales cycle restarts. Existing customers are cheaper to sell to than new ones. The goal of the stage is to turn a one-time buyer into a recurring revenue stream.
The Customer's Mind: "I love this product. I want to tell my friends."
Goal: Increase customer lifetime value.
Tactics: Subscription models, loyalty programs, VIP communities, and referral bonuses.
Metric: Repeat purchase rate and churn rate.
AICCL Loop
The AIDA variation we’ve looked at above is known as AICCL. It is the dynamic loop — Awareness, Interest, Consideration, Conversion, Loyalty — that high-growth brands like SKIMS rely on in 2026. As discussed in our recent Brand Teardown, the loop is the secret weapon that backs digital marketing strategies of empire-building brands.
Awareness & Interest (high intent): Instead of chasing cold traffic, they use content strategies (like TikTok trends or product-led SEO) to filter for high-intent users.
Consideration & Conversion (technical pivot): It’s about marginal tweaks. As we noted in our analysis of SKIMS below, if your mobile product page is slow or complex, you lose the cart. You need to use geo-funnels (customizing currency and content by location) and diverse payment options to grease the slide from thinking about it to buying it.
Loyalty: When a customer is loyal, they buy again, and they refer friends. That referral creates new Awareness for someone else, restarting the loop without you spending a dime on ads.
Watch the full breakdown of how this loop built a billion-dollar brand here:
Bonus: Want the exact setup mentioned in the video? We’ve created a SKIMS-inspired checkout template that you can import directly into Funnelish.
[Get SKIM-Style Funnel Template Here]
Examples of Ecommerce Funnel Flows
The best way to understand the mechanics is to see them running. Let's look at three more real-world examples of high-converting funnels.
Quiz Funnel (High Personalization)
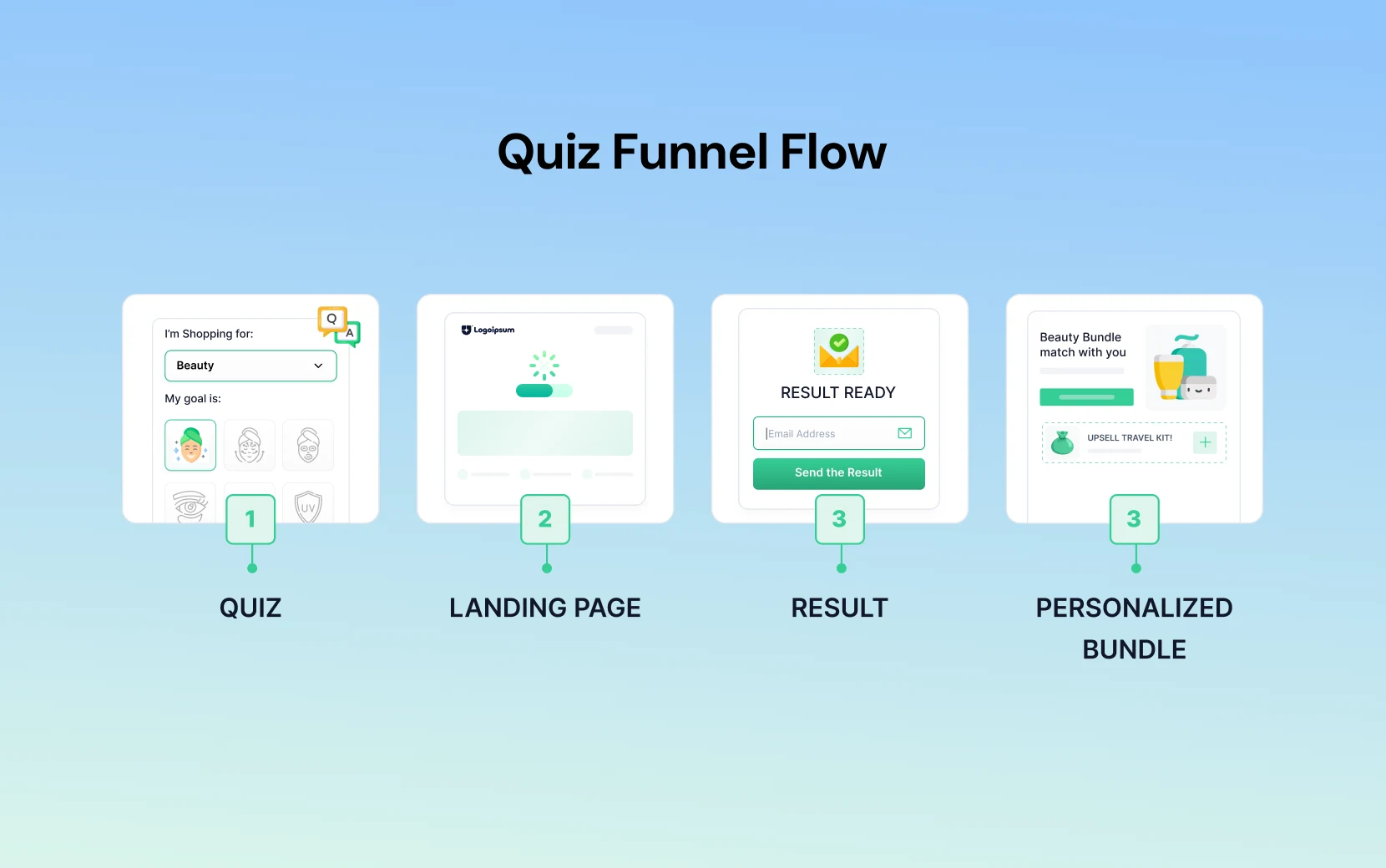
Best for: Skincare, supplements, coffee, pet food, etc.
This funnel works because it mimics a consultation. It trades the hard sell for helpful advice.
Traffic: An Instagram ad asks a provocative question: "Do you know your true skin type? Take the 30-second test."
Engagement: The user lands on a dedicated page (not the homepage) and takes a 5-question visual quiz. This collects zero-party data (data the user willingly gives you).
Lead gen: To see the results, the user enters their email. You now have a sales qualified lead.
Offer: The results page doesn't show a generic shop. It presents a perfect routine bundle for their dry and sensitive skin.
Upsell: After purchasing, they are offered a discounted travel-sized kit of the exact products they just bought.
Free Plus Shipping Funnel (High Volume)
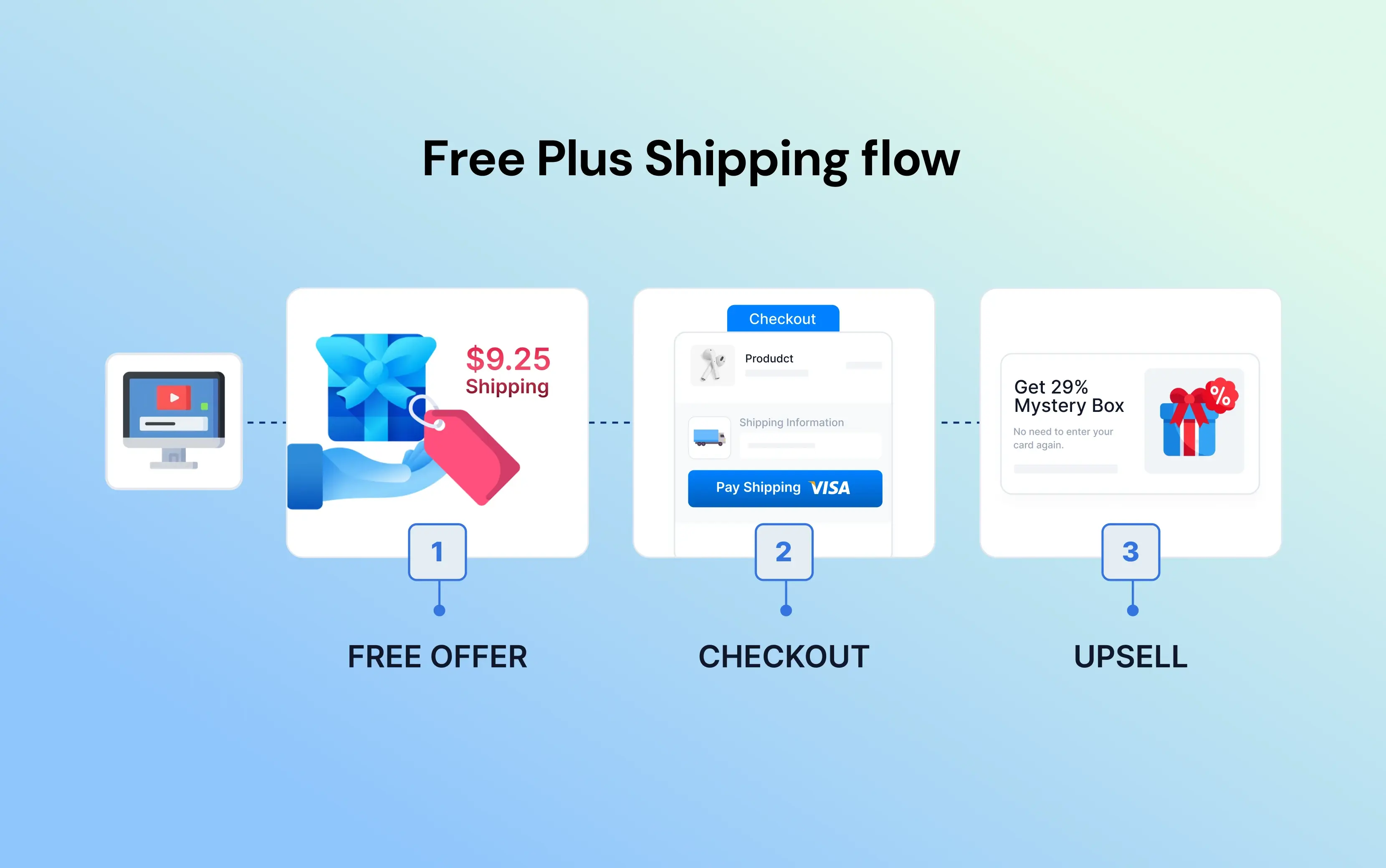
Best for: Low-cost gadgets, books, samples.
This sales funnel strategy uses the psychology of reciprocity and deals.
Traffic: A YouTube ad demonstrates a cool kitchen gadget that slices vegetables faster than other tools.
Offer: "Get this gadget for free, just cover the $9.95 shipping and handling."
Psychology: The user feels they are winning the negotiation. The barrier to entry is extremely low.
Real sale: Once they enter their credit card info, the funnel reveals the truth: the money is made on the backend. The funnel immediately offers a Mystery Box or a 3-pack of the gadget for $29.
Profit: The first item is a loss leader (you lose money or break even); the profit comes from the upsells.
High-Ticket Application Funnel
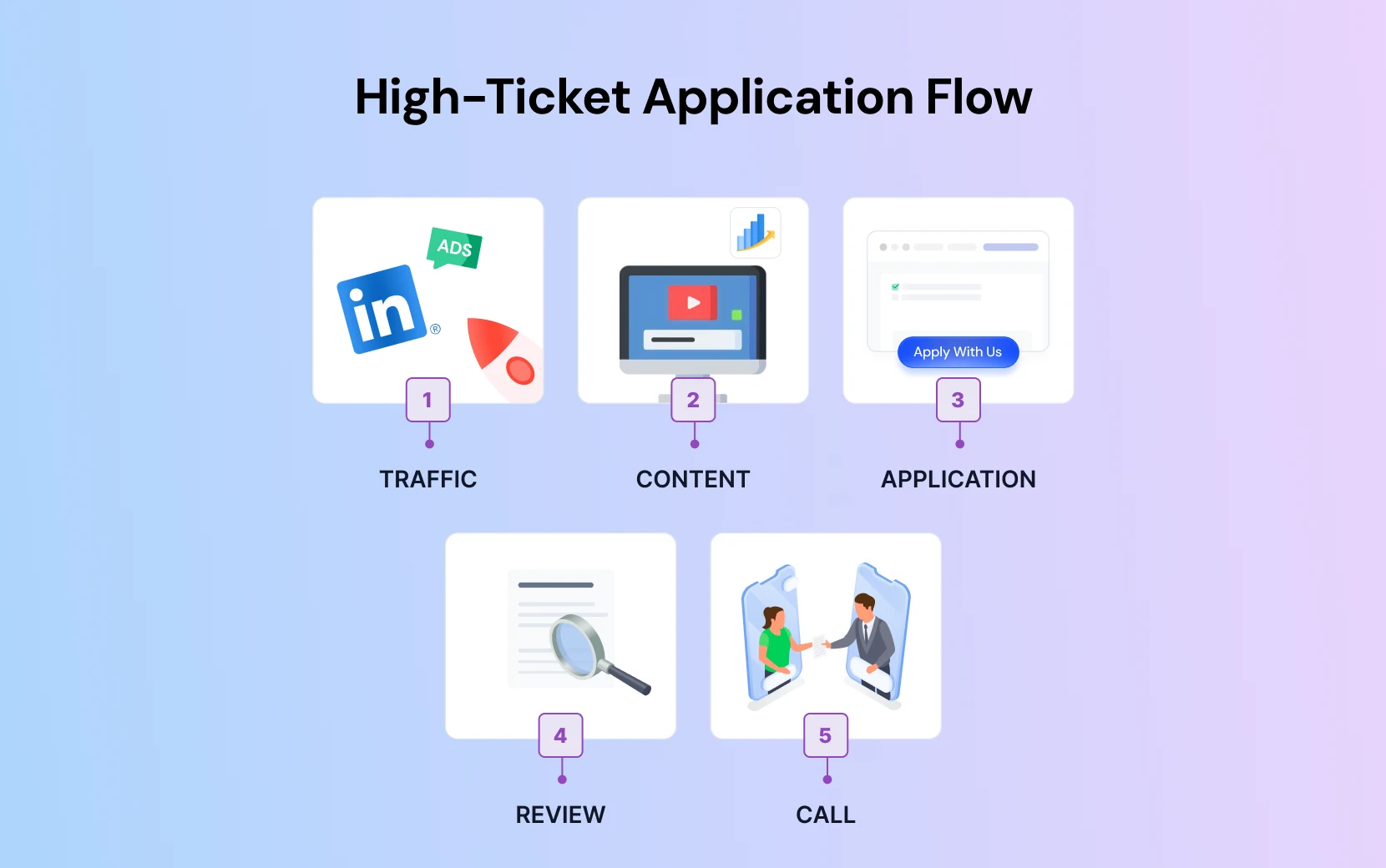
Best for: B2B services, expensive equipment, coaching, enterprise SaaS.
Traffic: LinkedIn ads or an SEO-optimized blog post.
Content: A comprehensive case study video or a video sales letter that proves expertise.
Filter: Instead of a "Buy Now" button, there is an "Apply to work with us" button.
Process: The prospect fills out a detailed form about their budget and needs. Sales reps review the data.
Close: A call is scheduled only for qualified leads.
This model relies on the sales team and sales automation to qualify leads before human contact occurs, saving hours of wasted phone time.
Sales Funnel vs. Website: Technical Reality
We touched on the psychology, but the technical distinction is another big thing for your sales funnel strategies.
A website is usually built on a CMS (content management system) like WordPress or a standard Shopify theme. It is meant for exploration and brand building. Plus, it carries code bloat — heavy code, large unoptimized images, and scripts that load slowly, especially on mobile devices.
A sales funnel is best built on a dedicated page builder like Funnelish.
Speed: Funnelish pages are optimized to load in under one second. In the mobile-first economy, speed equals revenue. Every 0.9 s can cost 0.4% in conversion rate. (Cloudflare) You cannot afford a slow site.
Isolation: A funnel page has no header menu. The user cannot wander off to read your blog, get bored, and forget to buy. They are tunnel-visioned on the offer.
A/B testing: You can test two different headlines simultaneously to see which converts better. A standard website makes this technically difficult; a funnel builder makes it a one-click process.
Which is better?
You need both. Your website is your brand's home base for organic traffic, press, and content marketing efforts. Your funnel is your laser for paid ads and marketing campaigns.
Sales Funnel Conversion Math Explained
A sales funnel is only as good as its numbers. You need to track the right sales funnel metrics to know if you are profitable. It is easy to get lost in vanity metrics (likes or page views), though. Instead, focus on the financial health of the funnel.
Key Metrics
CPA (cost per acquisition): How much ad spend does it take to get one sale?
AOV (average order value): How much does that customer spend in the first transaction?
LTV (customer lifetime value): How much do they spend over the next 1-2 years?
Cart abandonment rate: How many people leave at the last second?
To illustrate why these acronyms matter, let’s look at two businesses starting with the same $10,000 ad spend.
Scenario A is running a standard, unoptimized funnel.
Scenario B has optimized three key levers: cart abandonment, average order value, and lifetime value.
Compound Effect of Sales Funnel Optimization
Most businesses obsess over lowering their CPA with cheaper clicks. However, as the table shows, the real leverage is in the AOV and LTV.
In Scenario A, you are barely breaking even. One bad week of ad performance puts you in the red.
In Scenario B, the higher LTV allows you to actually bid higher for traffic to crush your competitors, because you know each customer is worth significantly more to you in the long run.
Golden Rule of Profitability
LTV > CPA
If your customer lifetime value is higher than the cost to acquire them, your business is viable long-term. However, with the rising ad costs, waiting 6 months to break even is risky. The goal for high-growth funnels is:
AOV > CPA
If you can be profitable on the first transaction, you can scale infinitely. This is why upsells and order bumps are key parts of an effective sales funnel. They increase the AOV without increasing the ad cost.
Sales Funnel Software + Tools
To build a successful sales funnel, you need a tech stack. Your e-commerce platform (Shopify or WooCommerce) is the engine room. It handles inventory, taxes, and fulfillment. But it is not a great sales floor, because it's rigid, generic, and slow.
Funnelish allows you to present a high-converting front end and keep your backend operations stable simultaneously.
Drag-and-drop builder: You don't need a developer. You can build landing pages that look like top-tier brands in minutes.
Deep integration: It syncs orders to Shopify, so your fulfillment team sees no difference. They just see an order come in; they don't know it came from a funnel.
Geo-funnels: You can show different content or currencies based on where the visitor is located. If a customer visits from the UK, show them GBP prices and a UK testimonial. If they visit from Texas, show USD. The relevance boosts conversion.
Performance: With fast page speed features, Funnelish ensures you don't lose customers to loading screens.
How to Build a Funnel with Funnelish in 2026
Ready to build? Here’s a step-by-step workflow to launch a high-performing eCommerce funnel. In 2026, funnels aren’t “pages”—they’re conversion systems. The goal is simple: turn paid traffic into profit fast, then iterate based on data.
Start with intent, not personas
Instead of over-engineering buyer personas, focus on intent. Ask: Why is someone clicking this ad right now? Funnels perform best when the message, page, and offer align around a single problem and a single promise.
In Funnelish: start with a proven funnel template, then match your headline and above-the-fold section to the exact angle your ad is using—so the visitor instantly feels like they landed in the right place.
Engineer the offer before the page
The offer does the heavy lifting. Winning funnels combine a core product with bonuses, bundles, or exclusive add-ons that make price comparison irrelevant. The goal is to make your offer feel uniquely valuable—not just cheaper.
Build your offer structure directly into the funnel experience using bundles, quantity breaks, and order bumps, so value is baked into the journey—not hidden in a menu or a product grid.
Build for speed first, design second
In a mobile-first, ad-driven environment, page speed isn’t a “nice-to-have.” It’s a profit lever. Even strong offers underperform when pages load slowly or feel clunky on mobile.
In Funnelish: you can launch instant-load landing pages built specifically for conversion traffic, helping reduce drop-off and protecting ROI—especially when scaling paid campaigns.
Use a frictionless, step-based checkout
A two-step checkout increases completion rates by reducing psychological friction and capturing customer data early. Even if a buyer doesn’t finish the purchase, you’ve created a follow-up opportunity.
Monetize after the “yes”
The real profit in funnels often happens after the initial purchase. One-click upsells and smart cross-sells can significantly lift AOV without requiring new traffic.
In Funnelish you can add post-purchase one-click upsells and downsells that feel native to the experience, so you increase revenue per customer without adding checkout friction.
Optimize based on revenue, not clicks
High-performing funnels are constantly refined. Don’t chase vanity metrics—optimize for revenue per visitor, AOV, and conversion rate across the full flow.
In Funnelish: run fast iteration cycles with A/B testing, adjust key levers (headline, offer stack, bumps, upsells, shipping logic), and scale what performs—without rebuilding your store or relying on dev work.
Common Sales Funnels Mistakes & How to Avoid Them
Even with the best sales funnel model, things can go wrong. Here are the most common pitfalls that kill conversions.
Mistake 1: Ignoring Speed
We cannot stress this enough. If your funnel takes 3 seconds to load, you have lost 40% of your traffic before they see your headline. Use tools that prioritize code efficiency.
Mistake 2: Weak Copy
Don't write like a robot or a corporation. Write like a human. Address the pain points as they are. Avoid jargon. If you confuse them, you lose them.
Mistake 3: No Follow-Up
Most people won't buy on day one. If you don't have an automated email sequence (retargeting) to bring them back, you are leaving money on the table.
Mistake 4: High Friction
Asking for too much info. Do you really need their phone number? Do you need their company name? If not, don't ask. Every extra field reduces your conversion rate.
Mistake 5: Disconnected Sales and Marketing
Your sales and marketing teams must align. If your Facebook ad promises a 50% discount, but the landing page shows full price (and requires a code), you break trust. The transition must be seamless.
Read more: 6 Ridiculously Easy Ways to Increase Your Funnel Conversion Rate
The Future is Funnel-First. Are You?
What more can we say about 2026’s demands? The spray and pray days of advertising are gone. To succeed, you should respect the stage of the funnel your customer is in and provide the exact solution they need at that moment.
Whether you are a solo entrepreneur or running a massive sales department, the principles remain the same. Build trust, remove friction, and maximize value. Your sales funnel begins the moment a stranger sees your brand. Make sure the journey is worth taking.
Want to maximize your sales success? Stop sending traffic to a slow store.
Get AICCL Template Here and build your first high-converting funnel today.
FAQ
What is a sales funnel?
It is the strategic engine that powers your customer lifecycle. Unlike a static website, a sales funnel coordinates your marketing and sales efforts to guide a stranger from their first click all the way to a purchase, filtering out window shoppers along the way.
What are the 5 stages of a sales funnel process?
The modern framework is Awareness, Interest, Decision, Action, and customer loyalty. Don't skip that last one. It's best to optimize every stage of the funnel — especially post-purchase — to turn one-time buyers into repeat spenders and referrals.
What is the 10-3-1 rule in sales?
It is a benchmark to help you manage expectations when you generate leads. The rule suggests that for every 10 leads entering your pipeline, about 3 will be qualified enough to consider your offer, and 1 will actually close.
Do sales funnels work?
Yes. Sales funnel important metrics — like conversion rate and AOV — are almost always higher because you remove distractions. The clarity creates satisfied customers because the path to the solution is simple and direct.
What is the 3-3-3 rule in sales?
In modern sales strategies, this refers to testing velocity: Test 3 new creatives, with 3 different headlines, across 3 different audiences to find the winner that scales.
What are common sales funnel mistakes?
A major mistake is treating sales funnels like static pages instead of optimization systems.
Many brands launch a funnel and never revisit it, missing opportunities to improve conversion rates, AOV, and retention.
Another common issue is sending the wrong traffic to the wrong funnel; cold audiences are often pushed to aggressive offers without enough context or trust-building, which kills performance before the funnel even has a chance to work.
What are the best sales funnel tools?
For eCommerce, Funnelish stands out as a true all-in-one platform. It combines an advanced yet easy-to-use drag-and-drop editor with the fastest page load speeds in the market - critical for paid traffic and mobile conversions.
Funnelish also offers deep Shopify integrations, built-in email and SMS sending, native upsells and order bumps, and even blog hosting directly within the platform. This allows brands to build, test, scale, and nurture customers without relying on a patchwork of external tools.
Do I need a website for a sales funnel?
A sales funnel can operate completely independently, especially when your focus is testing and scaling offers quickly. Funnels are designed to remove distractions and guide visitors toward a single outcome, which makes them ideal for paid traffic.
A traditional website becomes more useful later on, once you want a broader brand presence, content, and long-term customer relationships.
What is another name for a sales funnel?
Depending on context, a sales funnel may also be called a conversion funnel, offer funnel, revenue funnel, or demand funnel. Each term highlights a slightly different goal, but they all describe the same concept: guiding prospects step-by-step toward a purchase.
Which is better, a funnel or a website for sales strategies?
Most successful eCommerce brands use both, but for different objectives. Websites are optimized for discovery and organic traffic, while funnels are optimized for conversion and paid traffic.
Once brands identify winning products, they move them into dedicated funnels where faster page speed, controlled flow, upsells, and personalization consistently drive higher conversion rates and AOV than a traditional checkout.
Funnels consistently outperform standard eCommerce checkouts, often delivering 30% higher average order value and up to 3× higher conversion rates by controlling the customer journey, reducing friction, and layering in upsells and personalization.
Boost your eCommerce
sales today

24/7 support

No credit card required

Cancel anytime

24/7 support

No credit card required

Cancel anytime